5 fundamentals of the CAPA quality process
The CAPA quality process, in a nutshell, consists of the specific improvements a regulated organization makes to its processes to eliminate defects and non-conformities.
Effective CAPAs are the backbone of your quality management system, acting as the mechanism for fixing problems and optimizing your processes.
Robust CAPA management requires 5 key fundamental areas. Let's dive in and take a look at everything you need to know about the CAPA process.
CAPA meaning
The world of quality management is full of acronyms. SOPs. NCRs. GxP. And CAPAs. So what does 'CAPA' mean?
What does CAPA stand for?
CAPA stands for 'corrective and preventive action'.
As the name suggests, CAPAs are about problem-solving. And it's a two-step process: when something goes wrong, a CAPA is executed to fix ('correct') the immediate issue, then to 'prevent' it reoccurring with some tweak or improvement that addresses the cause.
CAPA definition
CAPA is defined as a systematic approach used in various regulated industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, and quality management, to identify, investigate, and address problems or non-conformities in products, processes and systems.
The purpose of CAPA is to rectify existing issues and prevent their recurrence in the future.
A CAPA system is therefore a crucial part of the modern quality management system, since quality in general is all about ensuring the integrity and quality of the products and services your company provides.
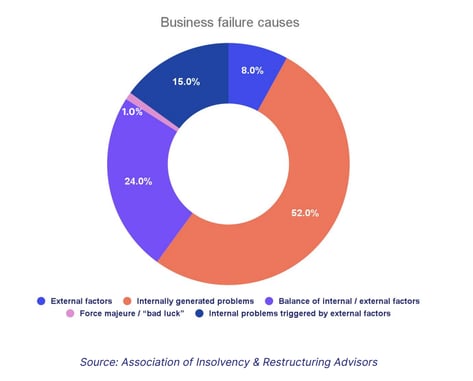
We can see how important this is when we consider that over half of the causes of a business failure can be attributed to internally generated problems that weren't properly addressed.
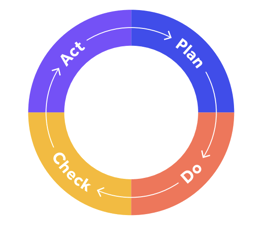
The Shewhart Cycle, more commonly known as Plan Do Check Act, is a classic quality management approach that enshrines CAPA procedures.
In this case, the 'check' and 'act' portions of the cycle are synonymous with CAPAs: systems and processes are checked, problems are found, then those problems are fixed with corrective and preventive actions.
What is CAPA?
What does a CAPA system or CAPA procedure look like in real life, then?
Remember, establishing a CAPA system requires a commitment to quality and continuous improvement. It's an ongoing process that helps you identify and resolve issues proactively, ensuring that your business operates efficiently and delivers high-quality products or services.
And it's not always something businesses get right.
CAPA requirements for medical devices marketed in the United States are laid out in FDA 21 CFR 820.100(a) - and failure to instil proper CAPA procedures is a consistent leading cause for FDA audit failure and the sending of Form 483s as a slap on the wrist.
FURTHER READING: 5 major CAPA medical device requirements
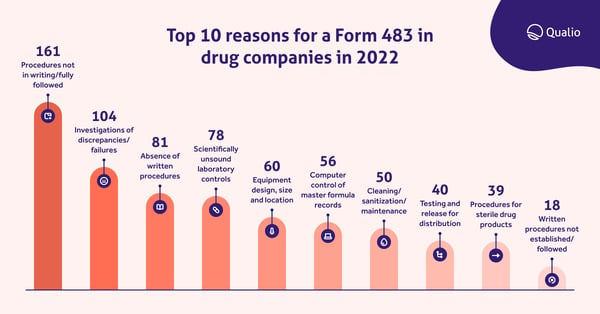
Our analysis of Form 483s sent to drug companies in 2022 found a similar pattern, with investigations of discrepancies and failures - a key part of CAPA, as we'll see below - the second-highest cause of Form 483 submissions.
Establishing a CAPA system
A robust CAPA management system needs a coordinated web of activity in place.
Start by determining the key steps and procedures for your CAPA system.
How will issues be reported, investigated and resolved?
What are the roles, responsibilities and accountabilities of the individuals involved in the process?
And most significantly - what reporting mechanisms can you get in place?
You can only correct and prevent faults that you know about, so it's vital that your organization has a system in place for fast, easy reporting that kicks off a CAPA process quickly.
This could be having a designated person(s) on-site for people to report issues to, or better yet an electronic cloud-based form for instant submission from anywhere.
You should proactively look for things to fix, too, so a robust internal auditing program needs to be established. Build a repeatable audit cadence that lets you interrogate key areas of your business and spot weaknesses, bottlenecks, defects and faults to which CAPAs could be applied.
Consider, too, how to keep an ear open to customer complaints. Complaints and complaint investigations are integral to an effective CAPA system, since they provide a source of external data to inform your CAPA processes once your device or drug has hit the market.
RELATED READING: How to build a complaint management system
Any effective CAPA system needs robust reporting, too.
Demonstrating 'improvement' by implementing CAPAs is a key regulatory requirement, cropping up in Clause 10 of Annex SL and, by extension, all modern ISO standards. If an auditor notes some non-conformances in a session, too, they'll expect to see documented evidence of how you've fixed them when they next visit.
A CAPA report is therefore a crucial ingredient to include in your CAPA strategy, since it proves you've effectively treated a defect with clear application of CAPAs.
Lastly, you should have clear targets in mind for your CAPA steps to be applied to.
Where should your CAPAs be applied? There are 4 key areas you should prioritize for your CAPA activity:
1. Facilities & people: equipment, manufacturing environment, etc.
2. Organizational system: documents, SOPs, quality controls, etc.
3. Processes: steps, outputs, handoffs, etc.
4. Product: specifications, integrity, characteristics, etc.
These 4 areas will provide over 90% of your day-to-day operational risks, so it makes sense to apply the bulk of your corrective and preventive actions there.
Tips for CAPA procedures
- Make your CAPAs SMART - that is, specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound.
- Clearly define roles and responsibilities for each stage of the CAPA process. Assign specific individuals or teams responsible for initiating, coordinating and tracking CAPA activities to completion. This ensures accountability and ownership, encouraging timely resolution.
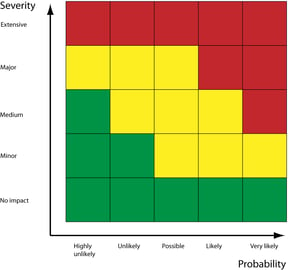
- Get a mechanism in place for classifying the issues you're addressing. CAPA application should be sensible and risk-based - there's no point throwing all your resources at a minor defect when there's a major fire to fight.
- Link your CAPAs to the severity, impact on quality, and potential risks of the issues they're addressing. This allows you to allocate resources tactically and address critical issues with the highest priority.
- Make CAPA awareness an evolving part of your company culture with training. Not only should all individuals with CAPA responsibilities be adequately trained, your entire organization should understand the importance of actively reporting issues so they can be fixed. Foster a culture of continuous improvement by encouraging employees to look for and report issues, and even to suggest improvement options themselves. Reward employees that take an active role here. Then ensure you regularly assess and enhance your CAPA strategy to adapt to your evolving organizational needs, such as when new products, processes and procedures are rolled out.
- A final tip is around optimizing your CAPA strategy. CAPA execution needs to be fast, accurate and controlled to have maximum impact and success. Manual or paper-based quality systems block visibility of quality issues and their root causes, making targeted CAPAs impossible.
One of our customers noted this very issue:
To accelerate and simplify your CAPA system and the execution of your CAPA procedures, more and more organizations are turning to CAPA management software.
To provide effective safeguards against regulatory risk, CAPA management is usually included as core functionality within a modern electronic quality management system (eQMS).
At a high level, any effective electronic CAPA system must:
- Let you build bespoke CAPA procedures which address your quality system requirements
- Facilitate data analysis to identify the sources of product quality issues
- Enable your organization to monitor trends for preventive action
- Integrate with other systems and QA processes to assure data quality
- Facilitate statistical analysis and formal failure investigations
- Allow your organization to validate the success of your preventive and corrective actions
LEARN MORE: 8 essential functions your CAPA software must have
With these tips in mind, let's take a look at the 5 fundamental steps of the CAPA quality process.
CAPA steps: the 5 fundamentals of the CAPA quality process
1. Detection
The problem identification and CAPA detection phase requires an appropriate documentation of the issue at hand. The description should be complete, including who, what, when, where, why, and how many.
Moreover, a risk analysis should be performed based on compliance risk. The results of the risk analysis should inform the CAPA timeline. In most cases, low-risk issues do not carry the same sense of urgency as high-risk issues.
2. Investigation & root cause determination
Next, your quality management team should commit to rapid investigation and root cause determination.
There are several methods for conducting root cause analysis, including:
- Brainstorming
- Flowcharting
- Fishbone diagrams
- Affinity diagrams
- Physics of failure
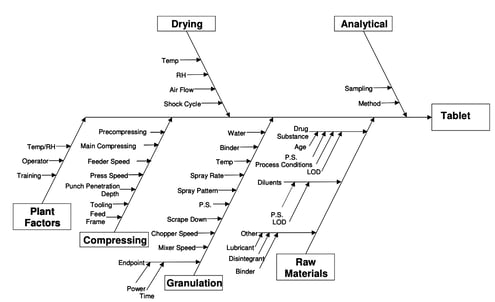
End-to-end traceability is crucial here. You should be able to track, and document, every root cause, change and applicable action step from the beginning to the end of your CAPA process.
RELATED READING: The 9 core elements of a quality management system
3. Proposed corrections
In this next phase, correction and containment should be completed as soon as possible to prevent further disruption.
Your organization should proactively review processes and procedures to identify broader issues. In the case of a product-related issue, field correction and/or recall may be required.
4. Implementation
At this point, long-term corrective and preventive actions work to resolve or eliminate the cause of nonconformity.
A corrective action is an action that eliminates the immediate cause of a nonconformity.
On the flipside, a preventive action eliminates the cause of potential future nonconformity.
RELATED READING: The 4 most common problems with CAPA processes
5. Verification of effectiveness
Finally, you need to validate and verify your corrective and preventative actions' effectiveness. Once a CAPA investigation is complete, determine if nonconformities have been resolved. Did it work?
You should also determine if your corrective and preventive actions haven't created new areas of inconsistencies.
For instance, any changes to your production process that were made to address an issue should also be seen as a new source of potential problems. Monitor your actions closely for a set period of time to ensure no adverse, unintended consequences occur.
Finding the best CAPA software for your company
Quality management issues have an immediate and significant impact on the success of your company. Failure to follow CAPA procedures and identify the root cause of compliance issues can cause repeatable problems at unavoidable costs.
What's more, ineffective complaint handling can jeopardize brand reputation and customer relationships. As a result, purchasing control breakdowns may be linked to unreliable input quality, and speeding through the validation will produce unfavorable results.
This is precisely why an electronic quality management system is a necessity. By adopting the right solution during the start-up or scale-up phase, you can build your organization a strong baseline for effective CAPA, supply chain management, and complaint handling.
Qualio is the first cloud-based electronic quality management system designed for growing life sciences organizations.
Schedule a demo today to learn more about how Qualio can help your organization embed world-class digital CAPA control.
