What is GxP in the life sciences industry?
GxP is a curious and crucial acronym which life science quality professionals will encounter at some point in their careers.
Three letters, one of them interchangeable, sum up the benchmark of quality that your regulated organization should aim for. GxP is a crucial ingredient of your quality and compliance efforts, so let's dive in and take a look at it in detail.
Table of Contents
What is GxP?
GxP is the bundle of quality guidelines and benchmarks that ensure your products and services meet a 'good' threshold of quality and integrity, and are safe for patient use.
GxP applies most readily to pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical organizations through the requirements of FDA 21 CFR Part 210/11, though medical device organizations may find some elements of GxP adherence useful for their day-to-day operations as well.
The FDA, along with input from the International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) and other agencies, developed GxP regulation to control the quality of FDA-regulated goods and help prevent life science disasters, such as the thalidomide tragedy in the late 1950s to early 1960s that caused thousands of birth defects.
Although an American innovation, GxP has infused into quality and compliance worldwide, manifesting in requirements from the EMA, MHRA, ISO and more.
GxP meaning
GxP looks like an unusual acronym with its mix of upper- and lower-case letters, but its meaning essentially boils down to 'good practice'.
GxP compliance encompasses a broad umbrella of quality management activities, and is vital for pharma companies to consider as they plan out their internal quality processes.
Although broad and variable by design, the GxP regulations focus particularly strongly and uniformly on data integrity, traceability and accountability. The guiding logic here is that airtight quality and compliance can't happen without a dependable and accessible baseline of information flowing around your business.
The GxP standards, although mandated under CFR Title 21, allow complying companies some flexibility to implement their own standard operating procedures - as long as they're following the overarching set of guidelines and regulations.
GxP regulations, in short, set the minimum requirements for life science quality management and give businesses a framework for continuous improvement to enhance their overall product quality.
What does GxP stand for?
GxP stands for 'good something practice'. The variable 'x' in the middle depends on the specifics of your operation: laboratory, distribution, documentation, manufacturing, and so on.
Because of this, GxP should be seen as a category of multiple good practices, rather than a monolithic benchmark of compliance like an ISO standard. The 'x' is simply swapped out for each subset of GxP.
To illustrate this point, let's look at some of the most common GxP subsets.
Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP)
The most common GxP requirement for pharmaceutical companies. GMP helps ensure your products are made according to established quality standards. FDA GMP regulations surround all aspects of manufacturing, from where raw materials are sourced to how standard operating procedures (SOPs) are followed.
Because pharma GMP often changes and evolves to match the modern manufacturing environment, it's often accompanied by the letter 'c' to denote that it's the current iteration of good manufacturing practice.
Good Automated Manufacturing Practice (GAMP)
GAMP is really a subset of a subset: the application of automation to GMP.
The two criteria of automation and consistency can help define the strength of how 'good' your manufacturing practice really is.
For example:
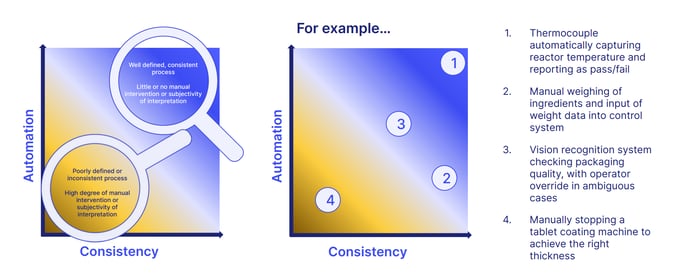
Here we can see how a well-defined, consistent and computerized process with no manual intervention would fulfil the requirements of GAMP much more effectively than lax, inconsistent processes which require manual input.
GAMP is now such an important part of GxP that the ISPE has its own GAMP Community of Practice, producing industry guidelines and coordinating annual networking events.
Their GAMP 5 guidelines were updated in 2022 to reflect the latest industry expectations of what computerized and automated good manufacturing practice looks like.
And it's precisely because regulators like the FDA want life science companies to embrace digitized, automated processes that their 2022 computerized system assurance guidelines were brought out.
By laying out sensible, risk-based validation (more on that later!) of automated computerized tools, the FDA wants to make adoption of digital life science quality management faster and easier than ever before.
More digital automating systems?
More GAMP.
Higher production volume and product safety.
Good Clinical Practice (GCP)
GCP outlines the planning and reporting of clinical trials that involve human subjects. It’s designed to ensure ethically-based practices and establishes a level of scientific quality. Adherence to this means that trial participants are protected as much as possible and that trial data is dependable.
Good Laboratory Practice (GLP)
Use GLP as part of your laboratory quality management system. GLP outlines the requirements for non-clinical studies done in a laboratory. These practices protect your research and help verify that the data that’s collected is accurate. Regulations include ethical treatment of animal subjects, type of facilities and equipment used during the studies, and cleanliness.
Good Documentation Practice (GDocP)
As we've touched on above, data and document integrity is a prominent component of GxP, and the requirements of Good Documentation Practice can be applied to any organization.
GDocP goes hand-in-hand with ALCOA+, a series of 9 data integrity benchmarks also introduced by the FDA.
To embed GDocP and ALCOA+ compliance, you should ensure that the documentation your business uses is:
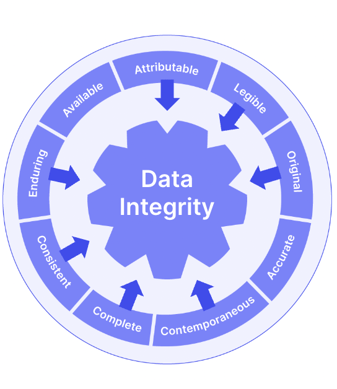
There are many other GxP regulation subsets, such as GSP (for storage), GDP (for distribution), and even some wonderfully niche and focused requirements like Good Tissue Practice (GTP) and Good Microbiological Practice (GMiP).
Each are important in their respective contexts to protect your business and the safety and efficacy of the products you provide to patients.
GxP documents
While we're on the topic of GDocP, it's worth taking some time to explore in detail the kind of documents you'll require for GxP compliance.
What does GxP compliance actually require day-to-day?
What sort of documents should you create, distribute and follow to embed GxP?
A robust and modern GxP pharma quality system, as you'd expect, requires a considerable documentation stack:
- SOPs and policies
- Quality records (including CAPAs, internal inspection reports and change control)
- CSA documents for computerized systems
- Training records
- Batch records
- Laboratory notes
- Bills of Materials (BOMs)
- Certificates of Analyses & Compliance (CoA/CoC)
- Quality Target Product Profiles (QTPPs)
- Logbooks
- Protocols
- Test methods
- Product/sample labels
Each GxP document format should each occupy a particular spot in your overall GxP control strategy and quality management system.
A typical GxP document structure could look like this:
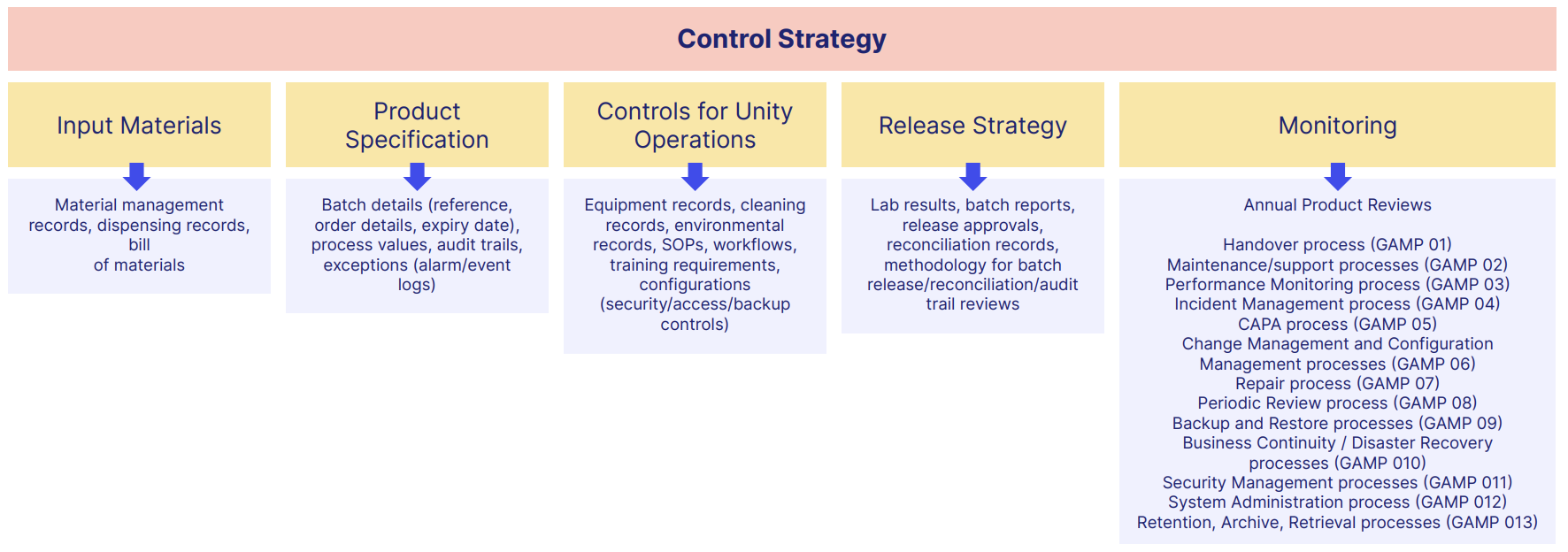
But as we've seen, how you manage and control these GxP pharma documents and their data is just as crucial as having them at all.
Paper, spreadsheets and legacy document management tools add unnecessary risk to your GxP quality management system by compromising GDocP and ALCOA+ principles - so you should invest in tools that support good document and data management.
There's no use getting a good GAMP system in place, only to let it down with leaky and uncontrolled documents.
FDA 21 CFR Part 11 compliance is a useful piece of legislation to consider as you tackle your GxP document management. Part 11 focuses specifically on how electronic records and signatures are managed and maintained in your company, and how data and digital security is embedded.
Part 11 is designed to give your business the framework to ensure that:
1. Data integrity and reliability is maintained for all electronic records that are created, modified, maintained, archived, retrieved or transmitted
2. The software and systems your business uses in its day-to-day activity are validated as appropriate and compliant
3. Your data is maintained safely and securely
4. Electronic signatures are non-disputable
5. Data changes can be tracked
6. Falsification of records is prevented and/or easily detected
7. Your electronic records are as trustworthy as a paper record
8. Your electronic signatures are as valid and legally binding as a wet signature
9 top tips for GxP document compliance with FDA 21 CFR Part 11
1. Build documented procedures (SOPs)
2. Build a workforce of trained and qualified individuals
3. Enforce limited role-based access with security controls
4. Enforce password policies
5. Link electronic signatures to records
6. Keep accurate and complete records (ALCOA+)
7. Protect and easily retrieve records throughout the retention period (ALCOA+)
8. Audit trails (ALCOA+)
9. Invest in an appropriate and validated electronic quality management system that automates these processes and benchmarks for you
GxP compliance
As mandated regulations, not following GxP compliance requirements can lead to severe consequences for your company.
Not only are they part of the FDA’s regulatory oversight, they also help to protect you from adverse events like:
- Product defects and recalls
- FDA Form 483s and warning letters
- Reputational damage
- Market rejection
- Customer complaints
- Fines and forfeitures from regulatory bodies
- Supply chain issues
Read our 4 scary life science quality management stories to see what happens without GxP in place
Like any quality management standard, GxP compliance brings powerful benefits: reliable manufacturing, higher product yield, faster marketization, happier customers and so on.
Not only is GxP compliance required to operate in key markets, it's the key to continuous improvement and long-term success for your life science organization.
This also applies to your broader supply chain, such as contract manufacturing organizations (CMO) and downstream distribution companies. If your entire supply chain isn’t following the basic GxP guidelines, you open your business up to compliance risk.
You should be careful, too, of conflating 'GxP compliance' with 'GxP certification'. Unlike an ISO standard such as 13485 or 17025, there's no GxP certificate you can mount on your wall.
The reward for GxP is regulatory approval and market access - not a certificate.
The 5 Ps
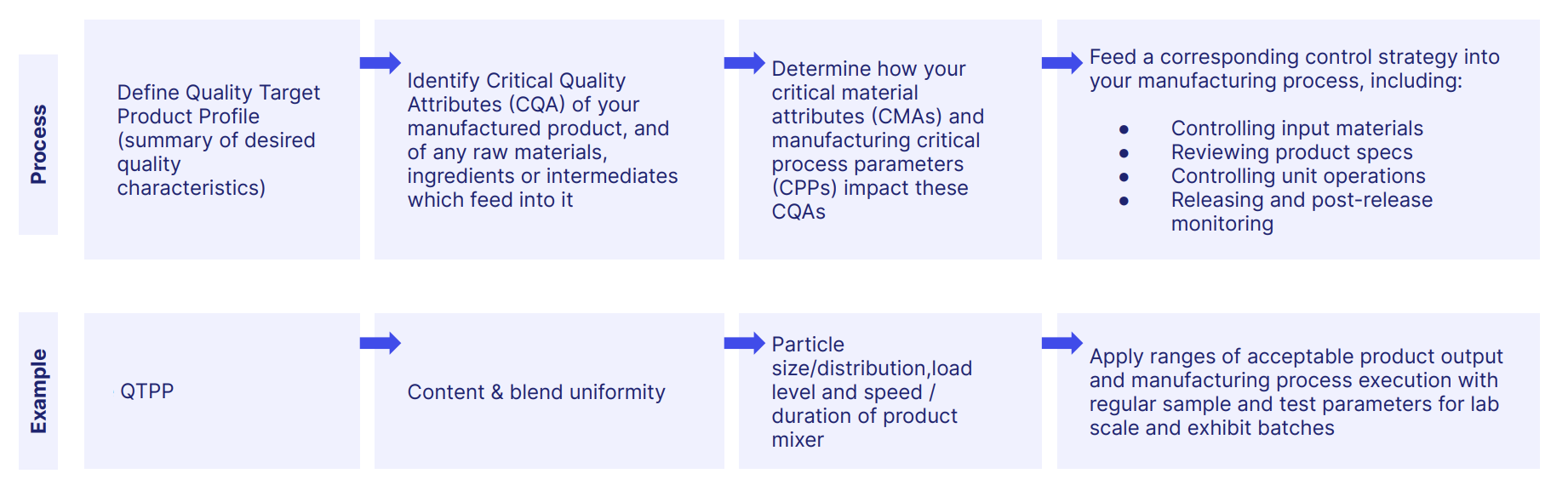
A useful way of planning GxP compliance and building an effective GxP system is to consider the 5 core ingredients of GxP regulation.
Since they're helpfully alliterative, they're also known as the 5 Ps.
Here they are.
People
The corporate cliché of people being the heart of a company is applicable to GxP compliance, too.
In short: your staff need to be properly trained and competent to execute clearly defined roles and responsibilities.
A robust training management system is therefore crucial.
Your people's daily work should be structured and managed by...
Procedures
All your business procedures need to be fully recorded and documented.
When people deviate from them or outputs diverge from expectations, there should be a clear mechanism in place to quickly investigate and correct any divergence.
This is the area of your business' GxP compliance where GDocP and strong document control are most vital.
Processes
Closely connected to procedures are processes.
GxP compliance is impossible without clearly defined and recorded processes.
All steps of your processes should be mapped out and, as we saw in the GAMP breakdown above, your processes should be as consistent, repeatable and automatic as they can possibly be.
Not only that, a careful balance of flexibility and fixity should be maintained. Strong change control should allow processes to be carefully molded and evolved as required, without them chaotically varying day-to-day.
Beware the deviation spiral of unstandardized processes!
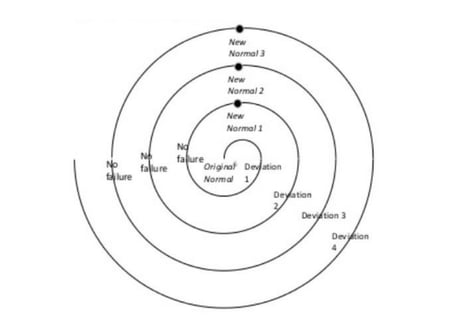
Watch our webinar recording: how to standardize your processes
Products
Pharmaceutical products can save lives, so GxP is crucial for maintaining their integrity.
All processes and procedures around your products, from manufacturing and packing to sampling, testing and distributing, need to be airtight.
And there should be clear specifications in place for the components and raw materials (inputs) that flow into your product, as well as the intermediate and finished products (outputs) you make from them.
TOP TIP:
Other quality benchmarks like the FDA's Quality by Design (QbD) framework and ICH Q8 can be helpful reference points for your GxP product lifecycle compliance. Do some wider reading.
GxP pharma product integrity can be maximized with some key documents and assurance steps.
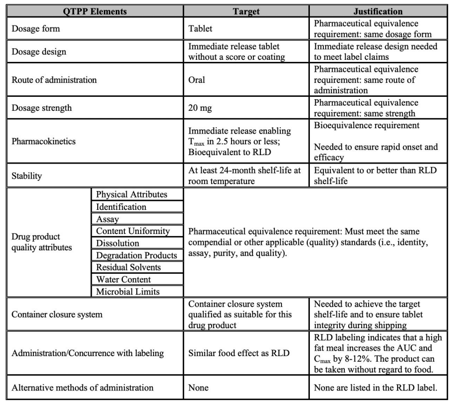
Your Quality Target Product Profile (QTTP) should map out the key desired characteristics of your product, and these should flow through your manufacturing process into your finished output.
Premises & equipment
Where your GxP activity happens is important, too: a filthy, unhygienic facility runs counter to the GxP aim of safe, effective life science products.
Your premises should therefore be regularly cleaned and maintained, with procedures in place to prevent cross-contamination.
The equipment you use needs to be calibrated and tested, with proper records and schedules in place to underpin this activity.
Your GxP equipment also needs to be validated. Which brings us to a key component of GxP compliance.
GxP validation
Validation is one of the most misunderstood and feared concepts within GxP.
What is GxP validation?
Remember the section about Good Automated Manufacturing Practice above? We touched on how regulators want GxP-regulated companies to embrace digital computerized tools that automate and accelerate product development and manufacturing.
GxP validation is the process where those computerized systems are tested before application.
After all, a computer system overseeing a GxP pharma system could cause death or serious injury if it were to glitch or malfunction.
In 1986, for example, the Therac-25 radiation therapy machine’s software bug meant cancer patients were blasted with radiation thousands of times stronger than intended, causing several deaths.
And in 2012, a piece of orphan code called a 'disabled function' in brokerage firm Knight Capital’s software systems was reactivated when someone saved some new code to the wrong location. They lost more than $400 million in just 45 minutes in the resulting trading system breakdown.
These are just 2 of dozens and dozens of examples of the power of faulty software to wreak havoc.
The FDA therefore mandates validation of GxP systems, and defines validation as follows:
The confirmation by examination… of objective evidence that software specifications conform to user needs and intended uses, and that the particular requirements implemented through software can be consistently fulfilled.”
GxP validation is about answering the question: is the software your business adopts fit for your intended use in your regulated GxP environment?
Although the old paradigm of computerized system validation (CSV) was perceived by many to be a headache, requiring weeks of testing and mountains of paper, the release of new computerized system assurance (CSA) guidelines shows a willingness from industry regulators to make the validation process as quick and easy as possible, while preserving risk awareness and maximizing patient safety.
A GAMP 5 editor discusses the latest changes to GxP validation
GxP compliance checklist
Need a hand with your GxP system compliance?
The Qualio+ team has built a handy 85-point GxP compliance checklist, structured around the 5 Ps, to help you embed robust and unshakeable GxP.
GxP software
While GxP compliance can seem overwhelming, the good news is that you can streamline your quality and compliance processes with GxP quality management software.
The right electronic quality management system, or eQMS, will help you document your GxP practices, train employees on them, embed repeatable action workflows, and more.
GxP software can help you:
- Manage CAPAs: An eQMS can document and manage corrective and preventive actions, driving continuous improvement and letting you plug gaps in your GxP compliance
- Embed GDocP and ALCOA+: Embed ALCOA+ and good document management principles with automatic version control, audit trails, review and approval workflows, and more
- Maintain FDA 21 CFR Part 11 compliance: E-signatures underpin key system activity like document review and training completion, giving you a secure and Part 11-compliant repository of GxP information
Get everything you need to be GxP-compliant with Qualio
If you’re just starting out on your GxP journey or are struggling to embed GxP compliance, using eQMS software such as Qualio can strengthen and accelerate your work.
Our software automates many of the tasks associated with GxP, including document approval reminders, training and e-signatures, while our expert Qualio+ team can support your regulatory requirements with ready-made document templates, expert advice, and more.
Contact us today for a demo of our GxP management software!

