Preclinical Testing of Medical Devices: 7 Essential Steps to Prepare
There are two very good reasons to get through the medical device regulatory approval process as quickly as possible: Profitability of your company and benefit to end-users. The quality managers who successfully navigate the approval process know the importance of getting their ducks in a row for each stage as they run the regulatory gauntlet.
Listen to the audio version of this article read by a real person here (Sound on!):
But that doesn't mean it's easy.
Clinical trial success rates in life sciences vary by category, but outcomes were sobering in 2018. The lowest-percentage pass rate last year for the ophthalmology category was just 3.4 percent. One major enterprise ended a phase II/III trial in June 2018 citing “serious” health risks for patients. Another enterprise ended a Phase I/II combination following a patient death.
If you aren’t properly prepared for preclinical testing of medical devices, there’s a chance you’ll experience a costly and highly publicized failure that puts patients at risk. More likely, your trial will be delayed, and you’ll experience a costly loss of competitive advantage. Remember, regulators aren’t trying to put up barriers to market approval. They’re simply trying to balance patient outcomes and safety.
By preparing well for medical device preclinical testing, you'll impress third party reviewers, secure the confidence of your team, and pass this important step with flying colors.
How to Prepare for Preclinical Testing of Medical Devices
Internal silos can be a barrier to fast regulatory approval. Too often, organizations have artificial barriers between preclinical, clinical, and manufacturing arms. Each of these parts of the organization may comply with cGMP, but they might not communicate. End-to-end transparency is critical to quickly usher your products through preclinical testing, clinical testing, and regulatory approval processes.
An enterprise quality management system (eQMS) can create transparency throughout the product life cycle by centralizing data on deviations, test results, and CAPA. Regulatory approval requires a strong data trail on the steps you’ve taken to ensure consistent product quality.
The easiest way to achieve this is with an eQMS like Qualio, which is built specifically for the life sciences industry. An organization-wide system for device data facilitates continuous improvement and strong documentation throughout the product life cycle. If your medical device company has between 5 and 500 employees, you'll find that our solution fits your needs. Learn more here.
1. Review the ISO 10993 Family of Standards
ISO 10993 is a family of 22 standards for evaluating the biocompatibility of medical devices. These standards encompass everything from evaluating and testing within a risk management process to animal welfare standards, and tests for system toxicity. Your medical device may not require all of these standards.
Familiarize yourself with the ISO system and best practices for testing, depending on your device’s complexity and risk profile. More information on navigating ISO 10993 is discussed below in the section on classifying your device within the biocompatibility matrix.
2. Start with User Requirements
A comprehensive list of user requirements for device inputs and outputs should be a starting point for effective testing. This is the foundation that can be used to trace the architecture of your testing program. It’s easy to overcomplicate testing by losing sight of what really matters—your customer. In addition to the customer’s story, allow predicate or “similar” devices to help you define characteristics and your testing requirements.
3. Understand the Impact of Toxicity
Don’t forget to consider the materials used to create your product as you approach medical device preclinical testing. Is your device manufactured using materials that have never before been tested on human subjects in a predicate device? Make sure there are sufficient datasets for mutagenicity and genotoxicity on each material, defined as the potential to cause mutations or toxicity. If there’s not a strong body of clinical evidence, it’s time to turn to ISO 10993-1:2018 to determine which material safety tests are needed.
If you find yourself in the position of needing to conduct your own mutagenicity and genotoxicity testing, you want to be as prepared as possible to dedicate enough resources. Establishing a baseline of toxicity and compatibility data can be resource-intensive, but it’s a necessary step. If you aren’t prepared with enough data or your inputs fail toxicity tests, your team could have to scratch your device design specs for a different material input.
4. Set Clear Metrics
Testing needs to effectively demonstrate a device’s benefit/risk profile. Two crucial metrics are safety and biocompatibility. However, these aren’t the only two metrics that matter in preclinical trials. Set standards to determine whether you need additional improvements, such as toxicity and biocompatibility metrics. These standards are critical if you need to engineer improvements in any areas where the device is lacking.
Determine which areas are relevant using ISO 10993 and standards for each area. Tests must be performed over a period of time that’s no shorter than a device’s intended use. Ensure your test data is deep enough to eliminate sample bias by selecting enough test subjects and controlling for the diversity of gender, body mass, organ mass, pathology, and other variables.
5. Categorize Your Device with the Biocompatibility Matrix
How do you know which standards from ISO 10993 apply? You need to classify your device according to the Biocompatibility Matrix. This is a framework for test design, not a checklist. The compatibility matrix should guide you to placing your device within three categories: surface design, external communications, and implant devices. Each of these three categories has additional subcategories; for nine possible places your device could fit into the biocompatibility matrix.
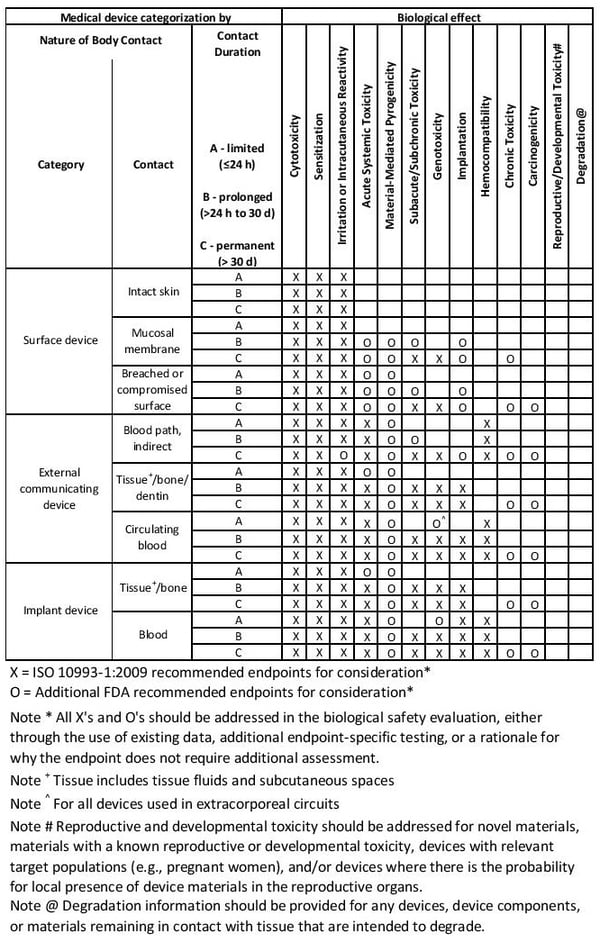
image credit: ISO 10993-1:2018
Examples and definitions for the biocompatibility matrix are further defined below.
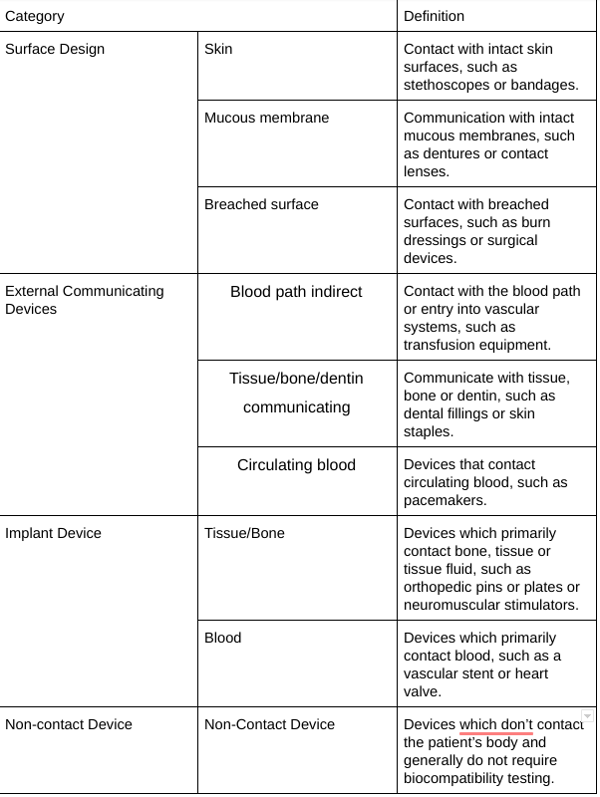
6. Gather Safety Data on All Components
Placing your device within the biocompatibility matrix will determine the types of data needed in preclinical testing. You may not be responsible for generating every data set required for clinical submission, however. There are several pathways to creating biocompatibility data on your materials selection, manufacturing processes, material composition, and sterilization methods.
- Use data from previous submissions with confirmation testing
- Use data from material and component suppliers with confirmation testing
- Use analytical data, following ISO 10993-18
- Use clinical trial data from predicate devices
7. Select a Reputable Medical Device Preclinical Testing Partner
Choosing a contract research organization (CRO) is important. The best medical device CRO is one who excels at tests and procedures on medical devices similar to your own. Evaluate a CRO’s history and reputation.
Once you’ve qualified a CRO based on experience, verify accreditation. Look for a CRO with a track record of:
- ISO 17025 Accreditation
- Successful client audits
- Regulatory compliance
- AAALAC certification
Nelson Labs, Toxikon, Element, and Namsa are four CROs that Qualio team members and partners have successfully used in the past.
RELATED READING: 4 Regulations That Apply to Medical Device CRO Selection
Preparing for Preclinical Testing of Medical Devices
Remember, regulators aren’t trying to put up barriers to market approval. They’re simply trying to balance innovation and patient safety. Streamlined progress through preclinical testing, clinical testing, and regulatory submission is easier with the right tests, the right data, and the right eQMS for managing information and processes.
How do you know which eQMS is the best for your medical device company? As a leading eQMS platform for startup and scale-up life sciences companies, a lot of our customers come to us after experiencing buyer's remorse because they made the wrong decision. So, we put together a free resource to help you find the right fit. Download 12 Questions to Ask Before You Buy an eQMS now.
